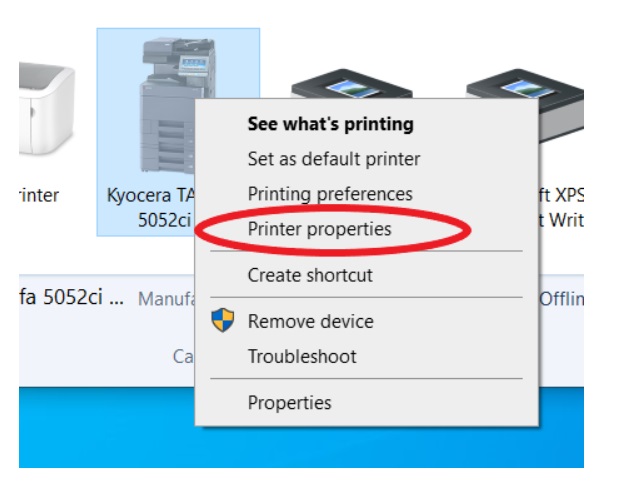
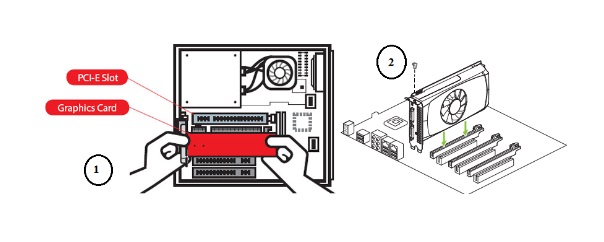
Aim :- How To Install A Sound Card
Tools Needed:
- Phillips screwdriver
- Anti-static wrist strap (optional, but recommended)
Steps:
Prepare Your Computer:
- Shut down your computer and unplug it from the power source.
- Open the case by removing the screws or sliding off the side panel.
Locate the PCI/PCIe Slot:
- Identify an available PCI or PCIe slot on your motherboard. The slot is usually located near the back of the case.
- Identify an available PCI or PCIe slot on your motherboard. The slot is usually located near the back of the case.
Remove the Slot Cover:
- If there’s a metal cover over the slot, remove it by unscrewing it or bending it slightly to break it off.
Insert the Sound Card:
- Align the sound card with the slot and press it down firmly but gently until it’s securely in place. Make sure the card's connectors are seated properly in the slot.
Secure the Sound Card:
- Use a screw to secure the sound card to the case, if applicable.
Reconnect Everything:
- Replace the side panel of the case and screw it back into place.
- Plug your computer back in and turn it on.
Install Drivers:
- Once the computer boots up, install the drivers for your sound card. You can usually find these on the manufacturer’s website or on the CD that came with the card.
Configure Audio Settings:
- Go to your computer’s sound settings to configure your new sound card and select it as the default playback device.







.jpeg)
















.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)

.jpeg)
.jpeg)