Projector - Introduction, Types And Works
A
projector is an output device that is capable of connecting to a computer,
which may be an other option for a monitor or television in terms of displaying
pictures to a large number of people. It takes images generated by a Blu-ray
player or a computer and projects them onto a large surface like a wall or
white screen. Projectors come in many shapes and sizes and are used in
conditions like a classroom, home cinemas, office training or presentation
sessions, etc. The projector looks like the below picture.
Projectors can be used for displaying pictures or videos
on the front or rear. The screen is the difference between both types of
projection, which is semi-transparent grey for rear projection and
non-transparent white for front projection. In the front projection, the
pictures are sent to the front of the screen from the audience. This process
does not need an empty space back side of the screen; therefore, this process
is most common.
In the rear projection, the pictures are sent from behind
the screen toward the audience. This method provides better contrast as
compared to front projection and is less affected by ambient light. Commonly
rear projection is used in commercial areas where more space is available and
also used in outdoor settings.
Types of Projector
The LCD (liquid crystal
display) and DLP (digital light processing) are two common types of projectors.
However, CRT (cathode ray tube) projector is another type of projector, which
was popular in the earlier times of projectors. In modern times, CRT projectors
are no longer in use; because they provided low light output and came in a
large size.
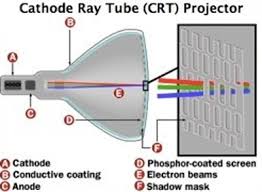
Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
A CRT, which stands for
Cathode Ray Tube projector, is a video projecting device that uses a cathode
ray tube (which is small and high-brightness) as the image generating element.
A Lens is kept in front of the CRT face through which the image is focused and
enlarged onto a screen. In the early 1950s, color CRT projectors came on the
market for the first time. Instead of a single-color CRT, most of the modern
CRT projectors have colored (red, green, and blue) CRT tubes and their own
lenses to generate color images and commonly come with color features. An
example picture of a CRT projector is given below.
CRT
projectors are not commonly in use today, as they consume high electricity and
are heavy in weight, and large in size. Also, they are not portable. Although
according to users, the picture quality of CRT projectors is brilliant, it may
be tricky and difficult to set up a CRT projector at the initial stage. As
compared to newer technologies, the projectors are capable of compatible with
new improvements; hence, they are nevertheless.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
An LCD projector is a type of projector based on liquid crystal displays, which is widely used in business seminars, presentations, and meetings. They utilize liquid crystal to display images, data or video, and function on trans missive technology.
LCD projectors have excellent color reproduction and are cheaper to produce, which makes them more popular as compared to many alternatives.
Generally, these kinds of display panels are used in many devices, such as cell phones, portable video games, Laptops, computers, and TVs. Comparing with CRT technology, the display in LCD technology is much thinner. The below picture represents how looks an LCD projector.
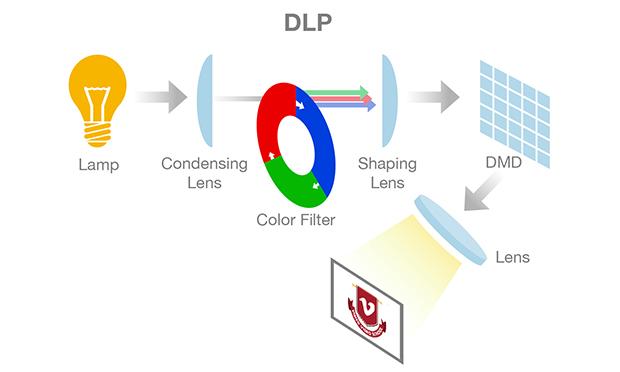
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
DLP projectors are utilized for front and back projection units and can be classified as one-chip or three-chip. Over 16 million colors can be produced by one-chip DLP projectors, whereas more than 35 trillion colors can be produced by three-chip models, which makes the projector capable of providing more lifelike and natural images. It is used in organizations and classrooms in terms of front projectors and also utilized for back projection in TVs. The below image is an example of a DLP projector.
DLP projectors are utilized
for front and back projection units and can be classified as one-chip or
three-chip. Over 16 million colors can be produced by one-chip DLP projectors,
whereas more than 35 trillion colors can be produced by three-chip models,
which makes the projector capable of providing more lifelike and natural
images. It is used in organizations and classrooms in terms of front projectors
and also utilized for back projection in TVs. The below image is an example of
a DLP projector.
How
a Projector Works
A
projector works with the help of a small transparent lens. There are various
technologies available that can display the images or objects from your source
media, like using lasers rather than LEDs.
The LCD projector was the projector type that was dominated by projectors primarily used for computer monitor mirroring and business presentations. Due to the tech became more common and available, they were also commonly used as television alternatives. Now, you have prism-like Digital Light Processing (DLP), mirror-based projectors, including the LCD/DLP hybrid projectors, which combine DLP prisms and LCD tech together.
What to look for in a Projector?
When
you are planning to buy a projector, you need to consider your specific goals
or applications and the price that you can afford. Mainly, determining your
budget is the best bet to buy a project. Also, you can adjust things according
to your requirements, whether you need a low-latency projector for online
first-person shooter gaming purposes or you are willing to torrent for a
particular type of projector. Your personal preferences and financial
circumstances should work to get you the right projector.
Uses for Projectors
Actually, the
applications of a projector depend on the projector type you have. Generally,
projectors can be used to project video, slides, and images onto a screen and
also used in business meetings, conferences, classrooms, and churches for
presentation. There are various kinds of projectors; some of them can be used
for different purposes, and even one projector can be used for some other
objectives. For example, mostly the use of a video projector is not uncommon,
which is usually used in home theaters. The main applications of projectors
used in daily life are given below:
- Educational and Classroom
- Home Theater:
- Advertising and Art Installation:









Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, please let me know