What is a computer system?
Definition:
"All the different pieces of electrical hardware that join together to make up the complete computer system."
A computer system is made up of 4 main types of components:
- Input Devices (keyboard, mouse etc)
- Output Devices (monitor, speakers etc)
- Secondary Storage Devices (hard disk drive, CD/DVD drive etc)
- Processor and Primary Storage Devices (cpu, RAM)
Examples of common Computer Hardware (components):
Features of Internal Hardware
Computer Components
Internal
computer components are designed to fit INSIDE the computer system and they all
carry out important roles. We will discuss the following:
- Motherboard (this does something with the data to make it useful information)
- Processor (central processing unit)
- Internal Memory (RAM and ROM)
- Video Card (aka graphics card)
- Sound Card
- Internal Hard Disk Drive
- The motherboard is central to any computer system.
]
- All components plug into the motherboard either directly (straight into the circuit board) or indirectly (via USB ports).
- Once connected to the motherboard, the components can work together to form the computer system.
- Components communicate and send signals to each other via the BUS Network.
Processor (CPU / Central Processing Unit)
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer.
The CPU 'controls' what the computer does and is responsible for performing calculations and data processing. It also handles the movement of data to and from system memory.
There are two main brands of CPU currently on the market... AMD and Intel:
Internal Memory (RAM and ROM)
There are two types of internal memory -
RAM and ROM.
- RAM and ROM are used to store computer data and this can be directly accessed by the CPU.
- RAM and ROM are sometimes referred to as 'Primary Storage'.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
- RAM is used to temporarily store information that is currently in use by the computer. This can include anything from word documents to videos.
- RAM can be read from and written to and so the information stored in RAM can change all the time (it depends what tasks you are using the computer for).
- RAM is a fast memory. Data can be written to and read from RAM very quickly. RAM is generally measured in GB (Gigabytes).
- RAM is Volatile Memory. This means that information stored in RAM is deleted as soon as the computer is turned off.
- The more RAM you have installed in your computer -- the faster it can perform. You can open and use more programs at the same time without slowing the computer down.
- ROM is used to permanently store instructions that tell the computer how to boot (start up). It also loads the operating system (e.g. Windows). These instructions are known as the BIOS (Basic input/output system) or the boot program.
- Information stored in ROM is known as READ ONLY. This means that the contents of ROM cannot be altered or added to by the user.
- ROM is fast memory. Data stored in ROM can be accessed and read very quickly.
- ROM is Non-Volatile memory. This means that stored information is not lost when the computer loses power.
- Other examples of ROM include:
- DVD/CD ROMS bought in stores containing pre-recorded music and movie files. These are played back at home but cannot be altered.
- ROM in printers which is used to store different font types.
Video Card (aka
graphics card)
Graphics cards are hardware devices that plug into the motherboard and
enables the computer to display images on the monitor.
Graphics cards usually require the installation of software alongside the hardware. The software instructs the computer how to use the graphics card and also allows you to alter settings to change
image quality and size.
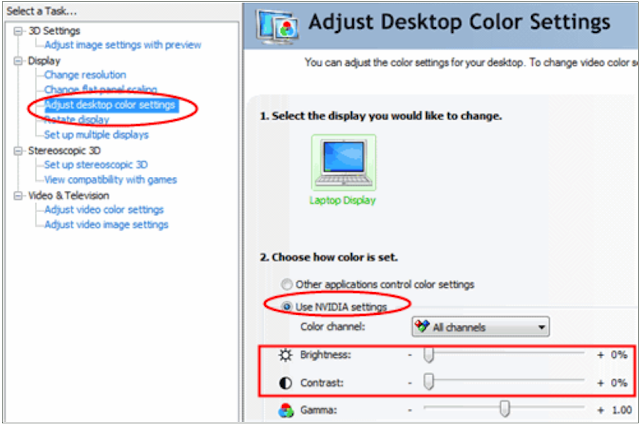
See below for an example of graphics card software allowing the user to
alter various graphical settings:
Sound Card
Sound cards are internal hardware devices that plug into the motherboard.
A sound card's main function is to allow the computer system to produce sound but they also
allow users to connect microphones in order to input sounds into the computer.
Sound cards are also useful in the conversion of analogue data
into digital and vice versa.
Storage
Devices (secondary backing storage)
Secondary
storage devices are used to store data that is not instantly needed by the computer.
Secondary storage devices permanently store data and programs for as long as we need. These devices are also used to back-up data
in case original copies are lost or damaged.
|
Remember: |
Temporary
storage like RAM does
not hold data for long periods. |
There are two categories of storage devices:
Internal Storage - Internal Hard Disk Drives
Features of External
Hardware Computer Components
External computer
components connect to a computer system from OUTSIDE. They are not necessary
for the system to function but make our experiences easier or better. We will
discuss the following:
- Input Devices (used to get data into a computer)
- Output Devices (used to get information out of a computer)
- Peripherals
Input Devices
- Input devices are pieces of hardware that get raw data into the computer ready for processing.
- Processing involves taking raw data and turning it into more useful information.
- Input devices fall into two categories:
- Manual Input Devices -
Need to be operated by a human to input information
- Automatic Input Devices
- Can input information on their own.
Output
Devices
When
inputted raw data has been processed it becomes usable information. Output
devices are pieces of hardware that send this usable information out of the
computer.
Some
output devices send information out temporarily and some send information out
permanently:
- Temporary Output Devices - E.g. Monitors which constantly refresh the outputted image on the screen
- Permanent Output Devices - E.g. Printers which output information onto paper as a hard copy.
Peripheral
Devices
Almost all input and output devices are known as 'Peripheral devices'.
These are 'non-essential' hardware components that usually connect to the system externally.
Peripherals are called non-essential because the system can operate without them.
For
example :
You
can still use your computer without speakers... you will just have to do
without high quality sound.







.jpeg)