What is Half Wave Rectifier?
In a half-wave rectifier, one half of each a.c input cycle is rectified. When the p-n junction diode is forward biased, it gives little resistance and when it is reversing biased it provides high resistance. During one-half cycles, the diode is forward biased when the input voltage is applied and in the opposite half cycle, it is reverse biased. During alternate half-cycles, the optimum result can be obtained.
Working of Half Wave Rectifier
The half-wave rectifier has both positive and negative cycles. During the positive half of the input, the current will flow from positive to negative which will generate only a positive half cycle of the a.c supply. When a.c supply is applied to the transformer, the voltage will be decreasing at the secondary winding of the diode. All the variations in the a.c supply will reduce, and we will get the pulsating d.c voltage to the load resistor.
n the second half cycle, the current will flow from negative to positive and the diode will be reverse biased. Thus, at the output side, there will be no current generated, and we cannot get power at the load resistance. A small amount of reverse current will flow during reverse bias due to minority carriers.
Characteristics of Half Wave
Rectifier
Following are the characteristics
of half-wave rectifier:
Ripple Factor
Ripples are the oscillations that
are obtained in DC which is corrected by using filters such as inductors and
capacitors. These ripples are measured with the help of the ripple factor and
are denoted by γ. Ripple factor tells us the number of ripples presents in the
output DC. Higher the ripple factor, more is the oscillation at the output DC
and lower is the ripple factor, less is the oscillation at the output DC.
Ripple factor is the ratio of RMS value of the AC component of the output voltage to the DC component of the output voltage.
DC Current
DC current is given as:
DC Output Voltage
The output DC voltage appears at the load resistor RL which is obtained by multiplying output DC voltage with the load resistor RL. The output DC voltage is given as:
Where,VSmax is the maximum secondary voltage
Form Factor
The form factor is the ratio of
RMS value to the DC value. For a half-wave rectifier, the form factor is 1.57.
Rectifier efficiency is the ratio of output DC power to the input AC power. For a half-wave rectifier, rectifier efficiency is 40.6%.
Applications of Half Wave Rectifier
Following are the uses of
half-wave rectification:
Signal demodulation: Half wave
rectifiers are used for demodulating the AM signals.
Signal peak detector: Half wave rectifier is used for detecting the peak of the incoming waveform.
Advantages of Half Wave Rectifier
Affordable
Simple connections
Easy to use as the connections are simple
Number of components used are less
Disadvantages of Half Wave Rectifier
Ripple production is more
Harmonics are generated
Utilization of the transformer is very low
The efficiency of rectification is low

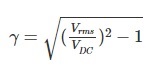


Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, please let me know