કેપેસિટર (Capacitor):
કેપેસિટર ઇલેક્ટ્રિક ચાર્જ સ્ટોર કરે છે. તે બેટરી જેવું લાગે છે તે ઊર્જાને અલગ રીતે સંગ્રહિત કરે છે. તે બેટરીમાં ઘણી ઉર્જાનો સંગ્રહ કરે છે. તે ખૂબ જ ઝડપથી ચાર્જ રિલીઝ કરે છે. કેપેસિટર ખૂબ જ ઉપયોગી છે તેથી જ તેનો ઉપયોગ તમામ સર્કિટ બોર્ડમાં થાય છે.
તે મૂળભૂત નિષ્ક્રિય ઘટકોમાંનું એક છે. તે અન્ય સર્કિટ ઘટકો જેમ કે ઇન્ડક્ટર અથવા રેઝિસ્ટર અથવા અન્ય સાથે અલગથી અથવા સંયુક્ત રીતે ઉપયોગમાં લેવાય છે. પરંતુ AC પાવર સર્કિટમાં તેનો ઉપયોગ પાવર ફેક્ટર કરેક્શનમાં થાય છે. તે એક બે ટર્મિનલ ઉપકરણ છે જે વિદ્યુત ક્ષેત્રમાં ઊર્જાનો સંગ્રહ કરે છે. તે બે સમાંતર પ્લેટો ધરાવે છે.
Capacitor stores electric charge. It is looks like battery it stores energy in a different way. It is stores much energy in battery. It releases charge very faster. Capacitor is very useful that’s why it is used in all circuit boards.
It is one of the fundamental passive components. It is separately or jointly used with other circuit components such as inductor or resistor or others. But in AC Power circuit it is used in power factor correction. It is a two terminal device which stores energy in an electric field. It is consisting of two parallel plates.
કેપેસિટરના કાર્યકારી સિદ્ધાંત(Working Principle of Capacitor):
Positive Q+ as Plate A and Negative Q- as Plate B,
પોઝિટિવ Q+ પ્લેટ A તરીકે અને નકારાત્મક Q- પ્લેટ B તરીકે,
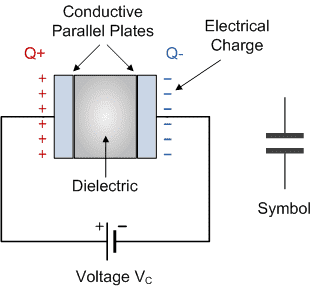
બે સમાંતર પ્લેટ A અને B ને ધ્યાનમાં લો, અને A વોલ્ટેજ સ્ત્રોતના હકારાત્મક ટર્મિનલ સાથે જોડાયેલ છે અને B સમાન સ્ત્રોતના નકારાત્મક ટર્મિનલ સાથે જોડાયેલ છે. ઈલેક્ટ્રોન નકારાત્મક ટર્મિનલમાંથી વહે છે અને પ્લેટ B પર એકઠા થાય છે અને નકારાત્મક ચાર્જ વિકસાવે છે, આ કારણે પ્લેટ Aમાં સમાન સંખ્યામાં હકારાત્મક ચાર્જ એકઠા થાય છે.
અહીં પ્લેટો વચ્ચેના ડાઇલેક્ટ્રિકમાં ઇલેક્ટ્રિક ક્ષેત્ર સ્થાપિત થાય છે. ઈલેક્ટ્રિક ફિલ્ડની દિશા હંમેશા ઈલેક્ટ્રોનને પોઝિટિવલી ચાર્જ્ડ પ્લેટમાંથી સ્ત્રોતના સકારાત્મક ટર્મિનલ તરફ લઈ જાય છે. પ્લેટ B પર સંગ્રહિત નકારાત્મક ચાર્જનું પ્રમાણ પ્લેટ A પરના સકારાત્મક ચાર્જના જથ્થા જેટલું છે. આને કારણે, બે પ્લેટ A અને B સમાન અને વિરોધી ચાર્જ વહન કરે છે, કારણ કે, આ બે પ્લેટોમાં એક વોલ્ટેજ છે.
ચાલો આપણે ધ્યાનમાં લઈએ કે સમગ્ર કેપેસિટરમાં વોલ્ટેજ Vc છે, અને તે લાગુ વોલ્ટેજ V ની વિરુદ્ધ છે. જેમ જેમ પ્લેટ પરનો ચાર્જ વધે છે તેમ, પ્લેટોમાંનો વોલ્ટેજ પણ એક સાથે વધે છે. તે જ સમયે, જો સમાંતર પ્લેટોમાંનો વોલ્ટેજ સ્ત્રોત વોલ્ટેજ V સુધી પહોંચે છે, તો પછી, સ્ત્રોતમાંથી ઇલેક્ટ્રોનનો પ્રવાહ થતો નથી.
Consider two parallel plates A and B, and A is connected with positive terminal of the voltage source and B is connected with a negative terminal of the same source. The electron flows from negative terminal and accumulates on the plate B developing negative charge, due to this the equal number of positive charges accumulate in plate A.
Here the electric field is established in the dielectric between the plates. The direction of electric field always drives electrons from the positively charged plate to positive terminal of the source. The amount of negative charge stored on plate B is equal to the amount of positive charge on the plate A. Due to this, the two plates A and B carry equal and opposite charges, since, there is a voltage across these two plates.
Let us consider voltage across the capacitor is Vc, and it is opposite that of applied voltage V. As the charge on the plate increases, the voltage across the plates also increases simultaneously. AT the same time, if the voltage across the parallel plates reaches to the source voltage V, then, there is not flow of electrons from the source.
Thanks sir
ReplyDeleteગુજરાતીમાં સમજાવવાની CAPACITY ઘણી !
ReplyDeleteહસાવતા આવડે છે? - હસમુખ પા.. /;૦)
Thank you for taking a few moments out of your precious time to comment and appreciate the blog.
DeletePost a Comment
If you have any doubts, please let me know